The Port Chicago disaster of 1944 serves as a stark reminder of the devastating consequences that can arise when safety protocols are neglected and systemic inequalities are ignored. This tragic event, which resulted in the loss of hundreds of lives, exposed critical deficiencies in training and safety practices, particularly for the African American sailors handling munitions. While Resuscitation Quality Improvement (RQI) programs as we know them today were not in place at the time, the core principles of RQI—continuous improvement, consistent training, and a focus on minimizing risk—were desperately needed at Port Chicago. This article will explore the historical context of the disaster, analyze the factors that contributed to the tragedy, and discuss how modern naval training programs, including the implementation of RQI in Port Chicago, have evolved to prioritize safety, address systemic issues, and honor the legacy of those lost.
Key Takeaways
- Consistent CPR training is essential for quality care: Regular practice with real-time feedback, like that provided through RQI, significantly improves skill retention and ensures healthcare providers are always ready to respond effectively in emergencies.
- Safety protocols are paramount in high-risk environments: The Port Chicago disaster serves as a stark reminder of the tragic consequences that can result from inadequate training, unsafe working conditions, and systemic inequalities. Prioritizing safety and equitable treatment for all is crucial.
- Modern RQI programs reflect a commitment to continuous improvement: The Navy’s adoption of comprehensive safety management systems, operational risk management, and human factors training demonstrates a dedication to learning from past tragedies and preventing future incidents.
What is RQI? A Critical Safety Framework
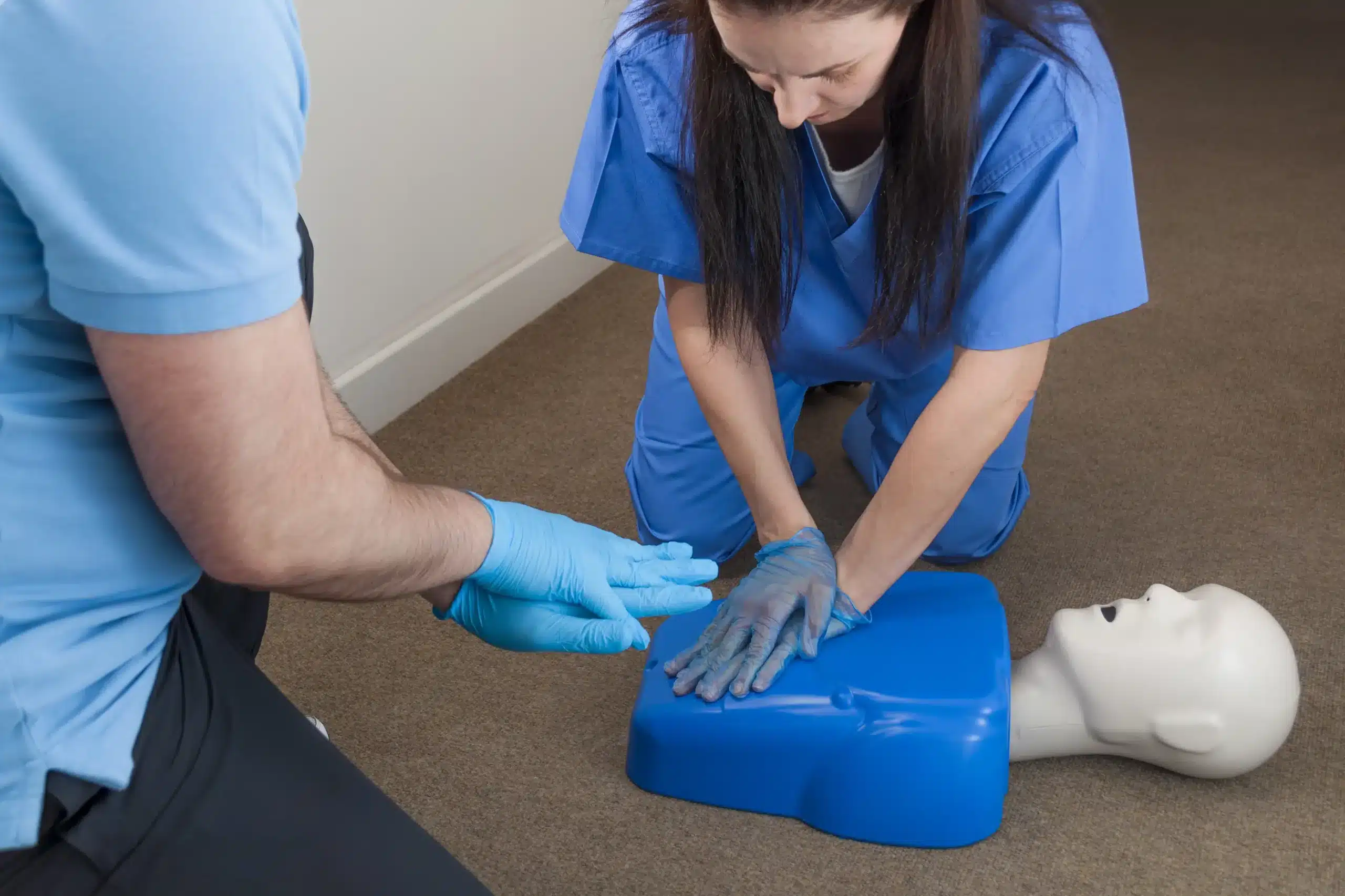
The Resuscitation Quality Improvement (RQI) program, developed by the American Heart Association (AHA), is a vital initiative designed to improve CPR quality. RQI focuses on consistent skill mastery through short, frequent training sessions. This helps healthcare providers maintain their CPR skills and confidently respond to emergencies. This approach tackles the common problem of skills decay, ensuring professionals are always ready. The AHA emphasizes how “RQI focuses on continued skills mastery with quarterly refresher sessions, a proven way to stave off skills decay” (RQI | American Heart Association CPR & First Aid).
This method not only reinforces essential skills but also uses real-time feedback so participants can constantly refine their technique. RQI is especially important in high-pressure environments where effective CPR can be the difference between life and death. A study in the Joint Commission Journal on Quality and Patient Safety highlighted how “The RQI program offers an innovative approach to maintaining competency for sustaining high-quality CPR skills.” This ongoing evaluation and feedback creates a cycle of continuous improvement, crucial for maintaining readiness in any field. Consistent feedback during training improves both skill retention and overall preparedness, as noted by Total Military Insight. RQI creates a critical safety framework that equips healthcare providers with the skills and confidence to handle emergencies effectively.
The Port Chicago Disaster: A Turning Point
The Port Chicago disaster, a catastrophic explosion at the Port Chicago Naval Magazine in California on July 17, 1944, tragically claimed the lives of 320 sailors and civilians, injuring hundreds more. The majority of those loading munitions were African American sailors working under unsafe conditions and lacking proper training. The Navy’s relentless emphasis on speed, including timed loading competitions, fostered a dangerous environment that ultimately led to the disaster. This tragedy exposed the urgent need for improved safety protocols and brought to light the stark racial discrimination faced by Black sailors.
The incident became a catalyst for change within the U.S. Navy, highlighting systemic inequalities that had long been ignored. The subsequent trial of the “Port Chicago 50,” who refused to return to work under such hazardous conditions, further underscored the issues of racial bias and the unjust treatment of African American servicemen. The Port Chicago disaster served as a pivotal moment, contributing to the eventual desegregation of the armed forces and raising awareness about the crucial importance of safety and equality in naval operations. The lessons learned from this tragedy continue to resonate, emphasizing the need for rigorous safety standards and the equitable treatment of all personnel. The Port Chicago Naval Magazine National Memorial now stands as a reminder of this tragic event and the fight for justice and equality that followed.
RQI and its Absence at Port Chicago
The Port Chicago disaster serves as a stark example of the tragic consequences that can occur when robust safety protocols are absent. While the concept of Resuscitation Quality Improvement (RQI) as we know it today didn’t exist in 1944, the core principles it embodies—continuous improvement, consistent training, and a focus on minimizing risk—were desperately needed. The explosion, which resulted in the deaths of 320 sailors and civilians, exposed critical deficiencies in safety practices and highlighted the devastating impact of inadequate training, particularly for the Black sailors handling munitions. These sailors were often given limited instruction, forced to learn on the job with dangerous materials, and subjected to discriminatory practices that undermined their safety. This lack of proper training contributed significantly to the disaster.
The Navy’s investigation following the explosion revealed a culture that prioritized speed over safety. The pressure to quickly load munitions onto ships bound for the Pacific theater of World War II led to rushed procedures and a disregard for potential hazards. This emphasis on rapid loading, combined with inadequate training and supervision, created a volatile environment. The racial discrimination prevalent at the time further exacerbated these issues, as Black sailors were often assigned the most dangerous tasks with minimal support. The subsequent court-martial of the Port Chicago 50, who refused to return to work under such unsafe conditions, underscored the systemic injustices these sailors faced. The incident became a turning point, forcing the Navy to confront its discriminatory practices and eventually leading to improvements in safety regulations and training. However, the legacy of Port Chicago remains a sobering reminder of the importance of prioritizing safety and ensuring equitable treatment for all personnel.
Inadequate Safety Measures: Analyzing the Port Chicago Tragedy
The Port Chicago disaster on July 17, 1944, remains a stark reminder of the inadequate safety measures within the U.S. Navy during World War II. The explosion, tragically claiming 320 lives, including 202 African American sailors, stemmed largely from unsafe working conditions and insufficient training for those handling munitions. A detailed account from the National Park Service describes the Navy’s investigation and the subsequent criticism regarding their handling of the incident, particularly the issues of racial discrimination and the lack of proper training and safety protocols.
Racial bias played a significant role in the tragedy. Reports indicate that officers considered Black sailors “unreliable” and incapable of understanding complex orders, leading to severely deficient training. This prejudice resulted in “on-the-job” training without comprehensive safety instruction, directly contributing to the devastating outcome. Declassified documents reveal the extent of this discriminatory practice and offer further context into the prevailing attitudes of the time. The disaster exposed not only the dangerous working conditions but also the deep-seated racial inequalities within the military. The Port Chicago disaster forced a reevaluation of safety protocols and training practices within the Navy, highlighting the urgent need for reform. The incident serves as a critical case study demonstrating the vital importance of adequate safety measures and the need to address systemic inequalities that compromise safety and effectiveness.
RQI Evolution: Lessons from Port Chicago
The 1944 Port Chicago disaster, a devastating explosion that killed hundreds of sailors, underscores the vital importance of rigorous safety protocols, especially when working with hazardous materials. The tragedy, rooted in inadequate training and exacerbated by racial discrimination, forced the Navy to re-evaluate its safety practices. This incident exposed critical gaps in munitions handling, highlighting the need for standardized procedures and comprehensive training. The ensuing trial and unjust treatment of the Port Chicago 50 further emphasized the systemic issues contributing to the disaster and ultimately fueled desegregation in the U.S. Navy.
Although Resuscitation Quality Improvement (RQI) didn’t exist then, the lessons from Port Chicago directly inform modern safety training. The disaster emphasized the critical link between proper training and accident prevention. Today, programs like RQI reflect this understanding by prioritizing regular, low-dose, high-frequency training. This research-backed approach builds and maintains crucial skills through consistent practice and real-time feedback, minimizing errors and promoting a culture of safety. The evolution from the tragic lessons of Port Chicago to modern training like RQI demonstrates a commitment to continuous improvement and recognizes that effective training is paramount to preventing future disasters.
Modern Naval RQI: Preventing Disasters
The Port Chicago disaster serves as a stark reminder of the importance of robust safety protocols in high-risk environments. Today’s Navy has implemented comprehensive RQI programs, incorporating lessons learned from past tragedies to prevent future incidents. These programs focus on several key areas:
Safety Management System (SMS)
Modern naval operations rely heavily on a comprehensive Safety Management System (SMS). This system provides a structured approach to managing safety risks, encompassing everything from hazard identification and risk assessment to incident investigation and emergency response. SMS emphasizes proactive measures, aiming to identify and mitigate potential hazards before they escalate into accidents. Clear communication and accountability are cornerstones of an effective SMS, ensuring that everyone involved understands their roles and responsibilities in maintaining a safe working environment.
Operational Risk Management (ORM)
Operational Risk Management (ORM) is another critical component of modern naval RQI. ORM is a decision-making process that helps naval personnel identify and assess potential hazards associated with specific operations. By systematically evaluating potential risks and implementing appropriate control measures, the Navy strives to minimize the likelihood and severity of accidents. This process involves considering various factors, such as environmental conditions, equipment limitations, and human factors, to develop strategies that balance mission accomplishment with safety. Evaluating the effectiveness of naval training programs is a key aspect of ORM, ensuring that personnel are adequately prepared for the challenges they face.
Human Factors Training
Recognizing that human error plays a significant role in many accidents, the Navy invests heavily in human factors training. This training aims to improve personnel’s awareness of how human limitations, such as fatigue, stress, and complacency, can impact performance and increase the risk of errors. By providing personnel with the knowledge and skills to manage these factors effectively, the Navy aims to create a more resilient and safety-conscious workforce. Integrating feedback into subsequent training iterations can enhance skill retention and mission preparedness.
Munitions Safety Training
The handling of munitions requires specialized training and meticulous adherence to safety procedures. The Navy’s munitions safety training programs emphasize the importance of proper handling, storage, and transportation of these hazardous materials. These programs incorporate lessons learned from past incidents, such as the Port Chicago disaster, to ensure that personnel are well-equipped to handle munitions safely and effectively. Rigorous training and strict adherence to safety protocols are essential to minimizing the risks associated with these inherently dangerous materials. The Navy quickly moved to investigate the cause of the Port Chicago explosion but faced criticism over its handling of the incident, particularly concerning the issues of racial discrimination and the lack of proper training and safety measures for the African American sailors tasked with handling dangerous munitions.
Effective RQI: The Role of Training
Effective resuscitation requires more than just initial training; it demands consistent practice and feedback to maintain crucial skills. This is where Resuscitation Quality Improvement (RQI) excels. Unlike traditional CPR training models that often involve lengthy, infrequent sessions, RQI focuses on short, targeted practice sessions distributed over time. This approach, combined with real-time feedback, has proven incredibly effective in improving both skill retention and overall competency. At Martinez CPR Classes, we emphasize the importance of ongoing training and offer RQI classes to help healthcare professionals maintain their skills and confidence.
Real-time Feedback and Skill Retention
RQI’s use of simulation stations with real-time feedback offers a distinct advantage. These stations provide immediate feedback on chest compression depth, rate, and recoil, allowing healthcare providers to refine their technique and correct errors as they happen. Studies show that this consistent practice with real-time feedback leads to significant improvements in CPR skill retention. One study found that nursing students who practiced with RQI maintained and even improved their compression and ventilation skills over six months, demonstrating the long-term benefits of this method. This consistent reinforcement helps build muscle memory and confidence, ensuring providers are always ready to deliver high-quality CPR. For healthcare providers in Martinez, Port Chicago, and Benicia, Martinez CPR Classes offers convenient access to these essential RQI training resources.
Competency-Based Approaches
RQI’s competency-based approach sets it apart from traditional CPR training. Instead of simply requiring course completion, RQI focuses on demonstrating proficiency in essential CPR skills. This means healthcare providers practice until they achieve a predetermined level of competency, ensuring they possess the skills and confidence to perform effectively in real-world emergencies. This focus on competency, combined with the frequent, low-dose practice sessions, helps solidify skills and maintain readiness. The American Heart Association recognizes RQI as an innovative way to maintain competency and sustain high-quality CPR performance, ultimately leading to better patient outcomes. This targeted approach ensures that healthcare professionals are not just certified, but truly competent in delivering life-saving care. We encourage you to explore our website for more information on our low price guarantee and group discounts.
Continuous Improvement: Shaping Naval Safety with RQI
RQI isn’t a static program; it’s designed for continuous improvement. This is crucial in a high-stakes environment like the Navy, where evolving technologies and operational demands require constant adaptation. Regular evaluation, feedback integration, and effective measurement are key components of this ongoing process.
Ongoing Evaluation and Feedback
Consistent evaluation is the cornerstone of any successful safety program. Analyzing training outcomes and the acquired skills helps the Navy ensure its training programs align with the ever-changing realities of naval operations. This feedback loop allows for adjustments to training methods, content, and frequency, ultimately enhancing mission preparedness. Integrating feedback from participants and instructors into subsequent training iterations can significantly improve skill retention and overall program effectiveness, as highlighted in Total Military Insight’s analysis of operational readiness training. This iterative approach ensures training remains relevant and impactful.
Measuring RQI Effectiveness
How do we know if RQI is working? The program’s effectiveness hinges on measurable improvements in resuscitation skills. RQI’s competency-based approach, emphasizing low-dose, high-frequency training, provides a framework for tracking progress. Studies demonstrate the impact of regular practice and real-time feedback on CPR skill maintenance. Simulation stations, with their ability to provide immediate feedback, allow individuals to refine their compression and ventilation techniques, ensuring they meet program standards. Regular practice has been shown to not only maintain but also improve CPR skills from baseline levels.
Overcoming Implementation Challenges
While RQI offers significant advantages, implementing it effectively does come with challenges. Integrating new training protocols into existing systems requires careful planning and execution. One common hurdle is maintaining system interoperability with real-world naval operations, as discussed in Total Military Insight’s exploration of Navy training simulations. The complexities of naval operations can create gaps between simulated training and actual operational readiness. Addressing these challenges requires a commitment to ongoing evaluation, adaptation, and a willingness to learn from both successes and setbacks. Just as incorporating feedback strengthens training, so too does addressing implementation challenges strengthen the overall impact of RQI on naval safety. By acknowledging and overcoming these obstacles, the Navy can ensure RQI remains a vital tool for enhanced safety and operational readiness.
RQI in Port Chicago Today: Honoring the Past, Securing the Future
The legacy of the Port Chicago disaster serves as a constant reminder of the importance of rigorous safety protocols and training. The tragedy underscored the devastating consequences of inadequate safety measures and the systemic issues that contributed to the horrific event. Today, the Navy has implemented extensive safety procedures to prevent similar incidents. These protocols prioritize the well-being of personnel and emphasize a proactive approach to hazard identification and mitigation. Modern safety standards, like those detailed in the Naval Safety Command’s guidance, stress the importance of addressing safety concerns before they escalate into accidents. This commitment to proactive safety management is a direct response to the lessons learned from Port Chicago.
Current Safety Protocols and Training
Current naval safety protocols encompass a wide range of measures, from stringent munitions handling procedures to comprehensive training programs. Regular drills and exercises reinforce these practices and ensure that everyone involved in operations understands their roles and responsibilities. The emphasis on meticulous planning and execution minimizes risks and fosters a culture of safety consciousness. The evolution of these protocols reflects a deep understanding of the human factors that contribute to accidents, as well as a commitment to continuous improvement. The goal is to create a working environment where safety is ingrained in the operational culture.
Diversity and Inclusion in Naval Safety
The Port Chicago disaster also exposed deep-seated issues of racial discrimination within the Navy. The subsequent trial of the Port Chicago 50, as documented in articles like this account of the disaster, brought to light the injustices faced by African American sailors. They were often assigned to the most dangerous jobs with inadequate training and support. The tragedy became a catalyst for change, ultimately contributing to the desegregation of the U.S. Navy, as detailed in the Port Chicago story. Today, the Navy actively promotes diversity and inclusion as essential components of a safe and effective fighting force. Recognizing the value of diverse perspectives, the Navy strives to create an environment where all personnel feel respected and valued. This commitment to inclusivity honors the memory of those who suffered at Port Chicago and strengthens the Navy’s ability to operate safely in a complex world.
Related Articles
- RQI Classes in Martinez, CA – Martinez CPR Classes
- Best Online ACLS Classes in Port Chicago – Martinez CPR Classes
- PALS Certification in Benicia: Your Complete Guide – Martinez CPR Classes
- BLS HeartCode Benicia: Your Certification Guide – Martinez CPR Classes
- American Red Cross in Martinez: A Guide to Giving Back – Martinez CPR Classes
Frequently Asked Questions
What exactly is RQI and why is it important?
RQI, or Resuscitation Quality Improvement, is a program created by the American Heart Association to help healthcare providers keep their CPR skills sharp. It involves short, frequent training sessions and real-time feedback, which helps people remember what they’ve learned and improve their technique. This is really important because in emergencies, good CPR can truly save lives.
How does the Port Chicago disaster relate to modern safety training?
The Port Chicago disaster, while a terrible tragedy, highlighted how crucial proper safety training is. It showed what can happen when people work in dangerous conditions without enough preparation and oversight. Though RQI didn’t exist back then, the disaster’s lessons about the importance of training and safety protocols directly influenced how we approach safety training today, especially in high-risk jobs.
What are some key elements of modern naval safety procedures?
Modern naval safety goes beyond just basic training. It includes things like the Safety Management System (SMS), which helps identify and manage risks, and Operational Risk Management (ORM), which helps people make smart decisions in potentially dangerous situations. There’s also a big focus on human factors training, recognizing that things like fatigue and stress can affect performance. And of course, there’s specialized training for handling dangerous materials like munitions.
How does RQI improve CPR skills compared to traditional methods?
RQI uses a different approach than traditional CPR training. Instead of long, infrequent classes, it uses short, regular practice sessions with feedback. This helps build muscle memory and confidence. The focus on competency, meaning you practice until you can perform the skills correctly, makes a real difference in how prepared people are for emergencies.
How does the Navy ensure its safety training programs stay effective and relevant?
The Navy constantly evaluates its training programs to make sure they’re up-to-date and effective. They look at what’s working and what’s not, and they use feedback from instructors and participants to make improvements. This ongoing process of evaluation and adjustment is essential, especially in a field like the Navy where technology and operational needs are always changing.